Exploring the Differences Between Investment Casting and Shell Moulding
When it comes to manufacturing precise metal components, two popular methods stand out: investment casting (lost wax process) and shell moulding. Both techniques have their unique advantages and applications, but understanding the differences between them is crucial for selecting the most suitable method for your project. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the differences of investment casting and shell moulding, highlighting their distinct features and benefits.
Investment Casting (lost wax Process): Precision and Complexity
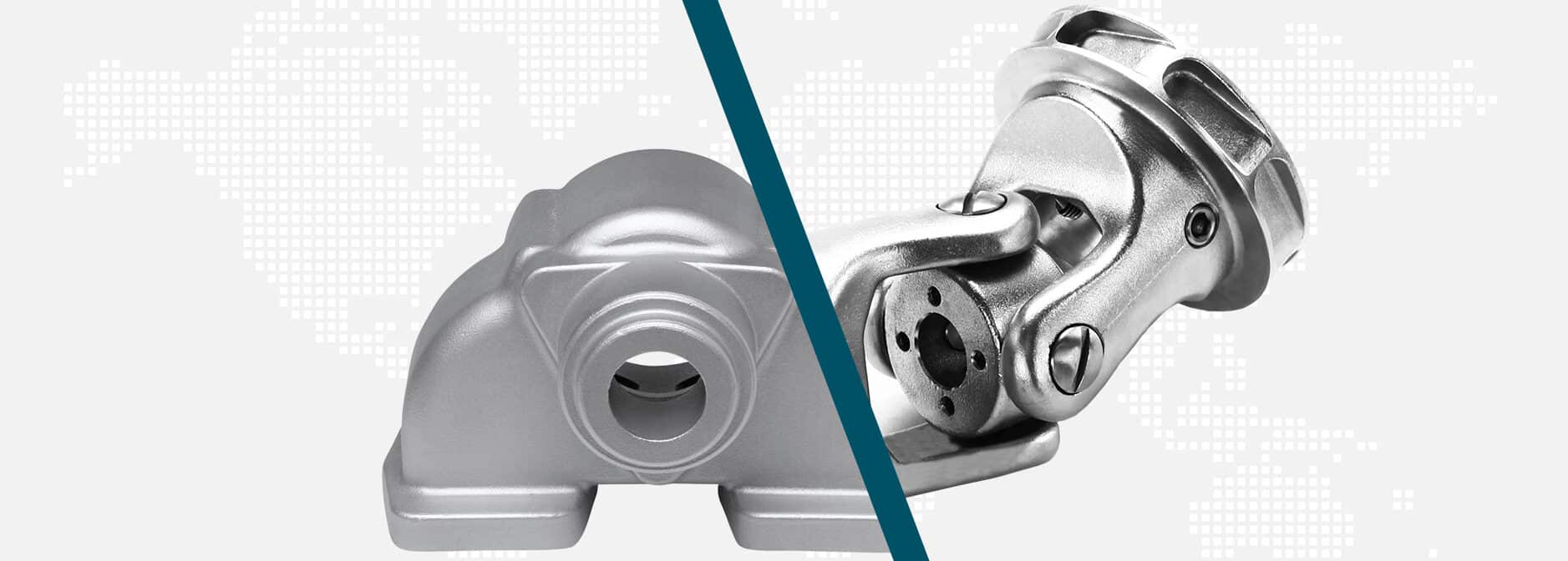
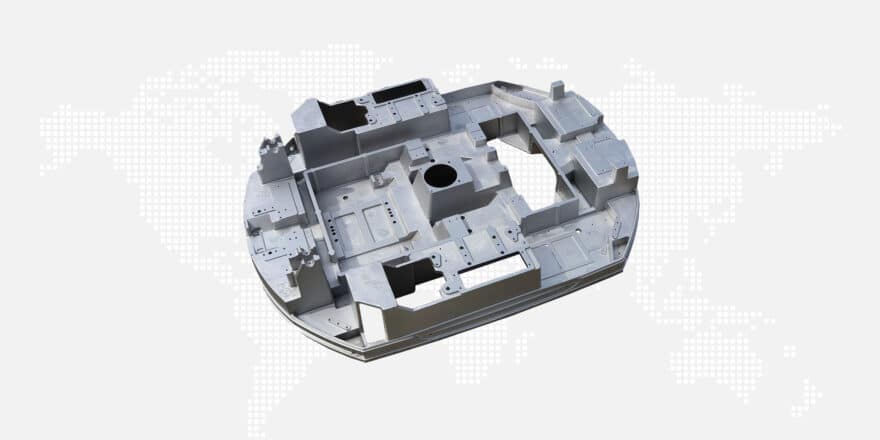
Investment casting, also known as the silica sol process, is a highly precise method for creating complex metal parts. This process involves creating a wax pattern of the desired component, which is then coated with a ceramic slurry made from silica sol. The coated pattern is then heated to melt out the wax, leaving behind a hollow ceramic shell. Molten metal is poured into the shell, and once cooled, the ceramic shell is broken away, revealing the final cast part.
One of the key advantages of investment casting is its ability to produce complex geometries and fine details, it (almost) does not need drafts the use of this ceramic slurry allows – the creation of smooth surfaces and tight tolerances. This makes investment casting ideal for manufacturing components with complex features, such as machining components, pumps, valves and rotor components.
Benefits of Investment Casting
- Higher dimensional accuracy and surface finish
- Ability to create more complex shapes and thin walls with almost no drafts
- Suitable for a wide range of alloys, including high-temperature materials
- Minimal post-processing requirements
Shell Moulding: Speed and Efficiency
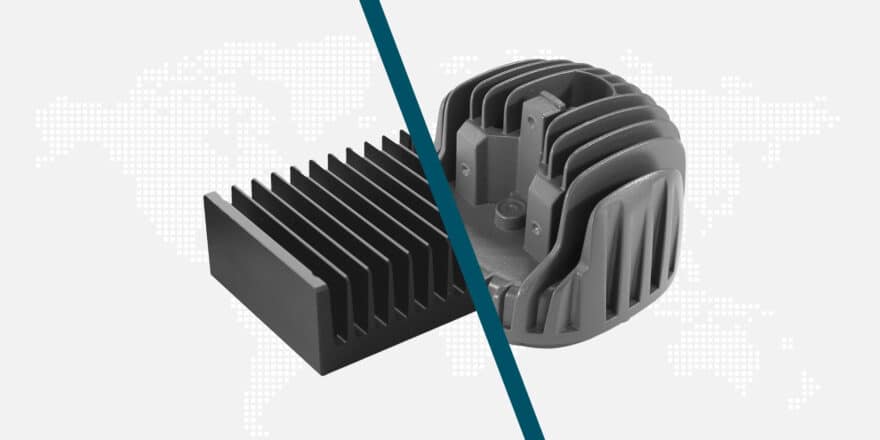
Shell moulding, on the other hand, is a faster and more cost-effective method for producing medium to high volumes of metal components. In this process, a heated metal pattern is coated with a mixture of sand and resin. The coated pattern is then cured, creating a thin, hard shell around the pattern. The pattern is removed, leaving behind a hollow shell mould. Molten metal is then poured into the mould, and once solidified, the shell is broken away to reveal the cast part.
Shell moulding is known for its quick turnaround times and efficient use of materials. The thin shell moulds require less sand and resin compared to traditional sand casting, resulting in reduced material costs. But it needs drafts. Additionally, the process allows to produce multiple moulds from a single pattern, making it suitable for higher volume production runs.
Advantages of Shell Moulding
- Faster production cycles compared to investment casting
- Cost-effective for medium to high volume production
- Good dimensional accuracy and surface finish
- Suitable for a variety of metals, including aluminium and iron alloys
Choosing Between Investment Casting and Shell Moulding
When deciding between investment casting and shell moulding, several factors should be considered. Investment casting is the preferred choice for components with fine details, tight tolerances, and complex geometries. It is also suitable for high-temperature alloys and parts that require minimal post-processing. However, investment casting typically has longer lead times and higher costs compared to shell moulding.
Shell moulding, on the other hand, is ideal for faster production cycles and medium to high volume runs. It offers good dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Detailing, tolerances and complexity little less than investment casting but Shell moulding is therefore more cost-effective than investment casting, especially for larger quantities.
Ultimately, the choice between investment casting and shell moulding depends on the specific requirements of your project, including the complexity of the part, the desired material, production volume, and budget constraints.
Conclusion
Investment casting and shell moulding are two distinct methods for manufacturing precise metal components. While investment casting excels in creating very fine and complex parts with high accuracy, shell moulding offers faster production times and cost-effectiveness for medium to high volume runs. By understanding the differences between these two processes, one can make informed decisions and select the most appropriate method for their specific needs.